Innovate
Your Software
Faster without Risk
Innovate Your Software Faster without Risk
Reducing Technical Debt with Feature Flags: A Developer's Guide
Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving world of software development, it's essential for developers to stay ahead of the curve. One aspect that can be challenging to manage is technical debt. This article will explore what technical debt is and how feature flags can help reduce it, ultimately making your development process more efficient and robust. Additionally, we'll briefly introduce FeatBit, a free and open-source solution for managing feature flags in your software projects.
What is Development Technical Debt?
Technical debt, often referred to as code debt or design debt, is a concept that originated in software development but can be applied to other fields as well. It refers to the accumulated costs and long-term consequences of taking shortcuts or making suboptimal decisions in the development process.
When developers prioritize short-term goals, such as meeting tight deadlines or accommodating last-minute feature requests, they may cut corners or use temporary solutions. These decisions may seem harmless at the time, but they can lead to complications later on. As a result, code becomes harder to maintain, modify, and debug, leading to an increase in the time and effort required to implement new features or fix bugs.
Technical debt can manifest itself in several ways, including:
- Poorly designed code architecture
- Inadequate documentation
- Duplicated or redundant code
- Unresolved bugs or performance issues
- Outdated technologies or dependencies
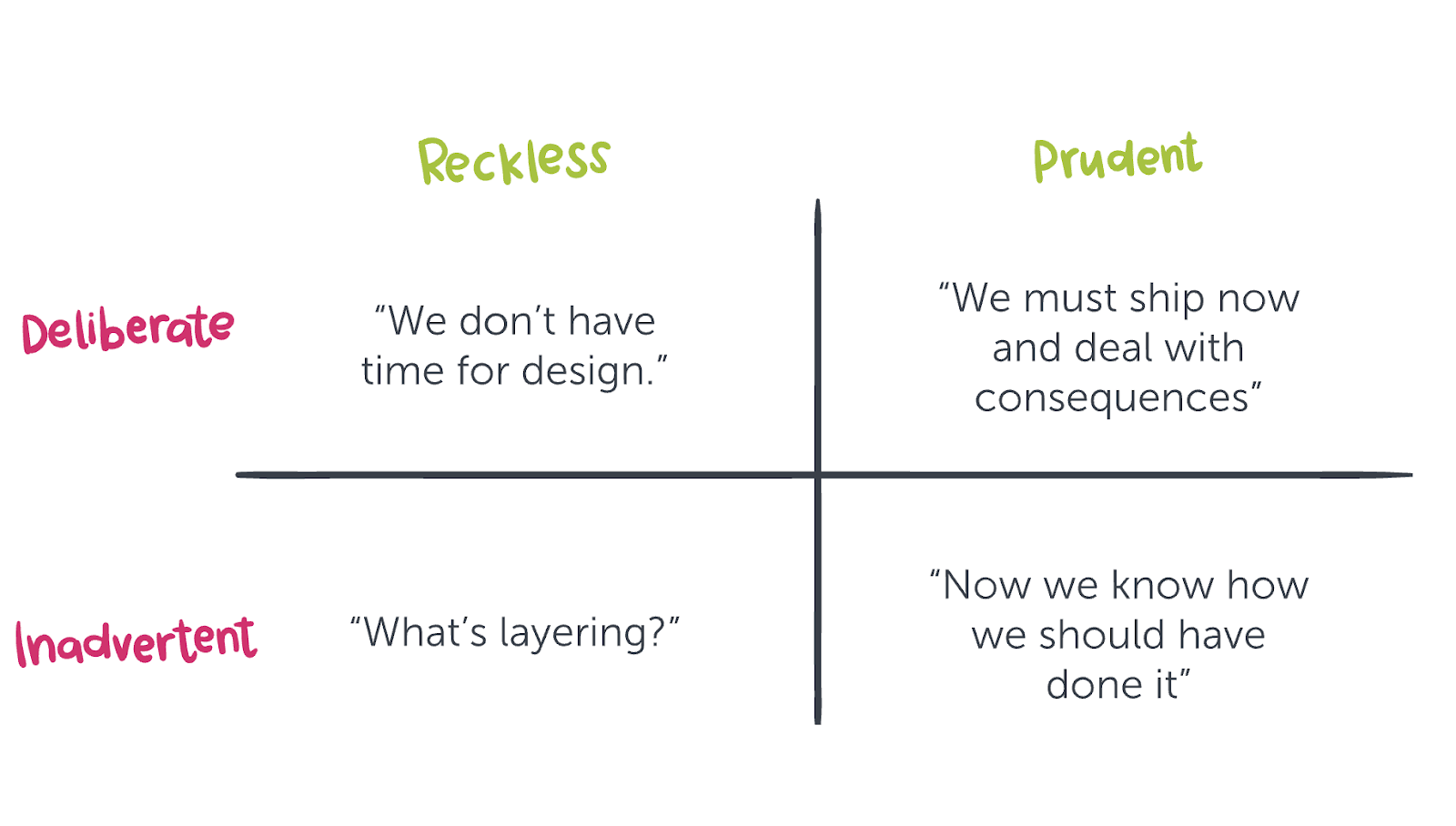
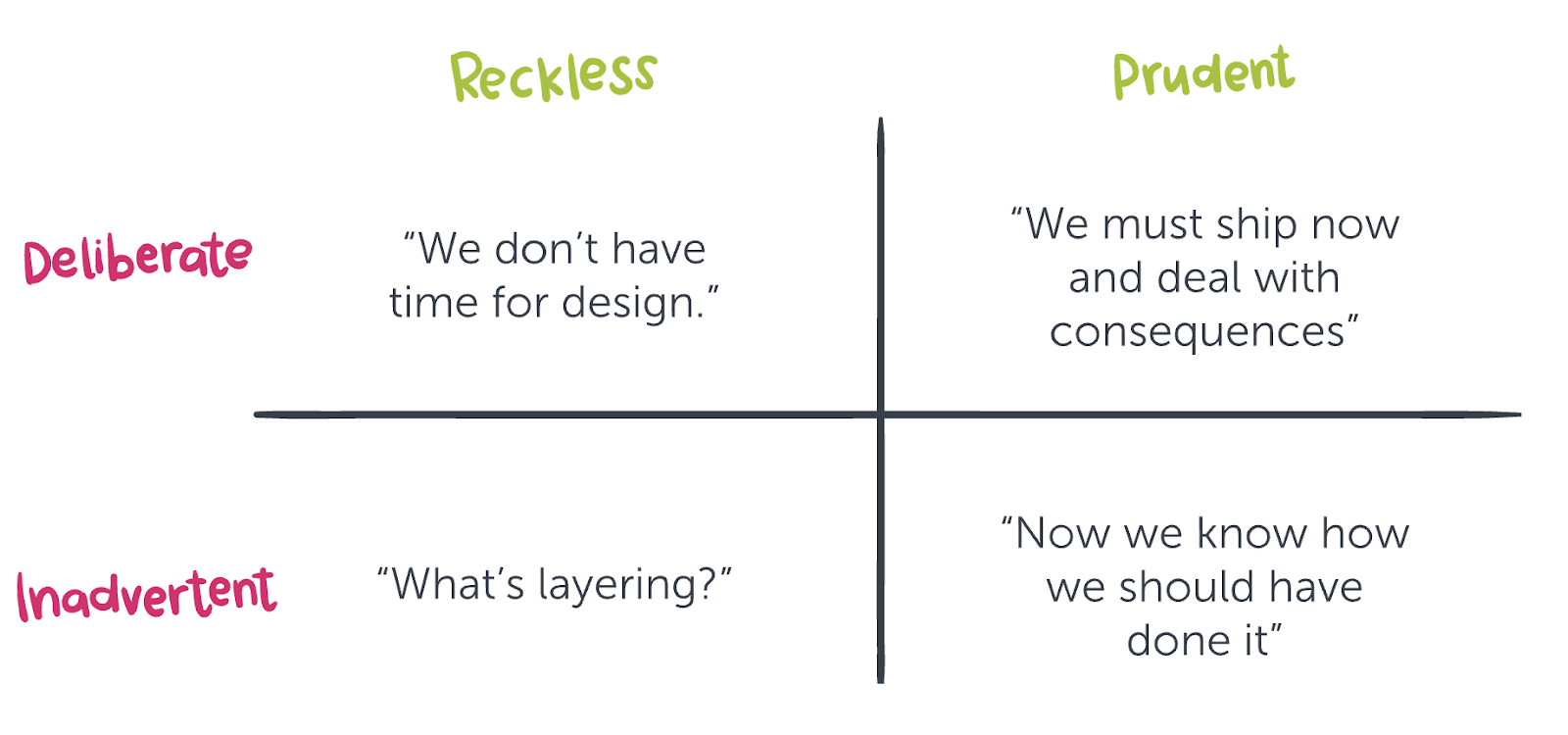
techDebtQuadrant.png
How Feature Flags Help Reduce Tech Debt
Feature flags, also known as feature toggles, are a development technique that allows developers to enable or disable specific features within an application. By leveraging feature flags, developers can manage technical debt more effectively and minimize the impact of suboptimal decisions. Here's how: While feature flags may not solve all forms of technical debt by themselves, they can aid in managing and mitigating some of the risks associated with it. Here's how feature flags can help address the different types of technical debt mentioned:
- Poorly designed code architecture:
Feature flags can facilitate the gradual refactoring of a poorly designed code architecture. By allowing developers to work on parts of the codebase without affecting the entire system, they can incrementally improve the architecture without causing disruptions. This approach provides a more controlled environment for optimizing the design and structure of the code.
- Inadequate documentation:
Although feature flags do not directly address inadequate documentation, they can indirectly contribute to better documentation by promoting a more organized development process. As feature flags enable incremental releases and testing, developers are encouraged to document their code more thoroughly to ensure smooth integration and a better understanding of the changes introduced by the feature flags.
- Duplicated or redundant code:
Feature flags can help reduce duplicated or redundant code by enabling developers to work on different versions of the same feature simultaneously. This allows for a more streamlined development process and encourages developers to reuse code instead of duplicating it. By using feature flags, developers can merge or disable redundant code more easily, leading to a cleaner codebase.
- Unresolved bugs or performance issues:
Feature flags enable developers to release and test features incrementally, which can help identify and resolve bugs or performance issues more effectively. By isolating the feature, developers can focus on debugging and optimizing it without affecting the overall system. Additionally, if a feature introduces new issues, feature flags allow for quick rollbacks, minimizing the impact on end-users and the overall system.
- Outdated technologies or dependencies:
While feature flags may not directly resolve outdated technologies or dependencies, they can provide a safer environment for updating or migrating to new technologies. By using feature flags, developers can gradually introduce new technologies, test their compatibility, and ensure that the migration does not disrupt the system. This approach allows for a more controlled and less risky transition to updated technologies or dependencies.
Introducing FeatBit: A Streamlined Open-Source Solution for Feature Flags
FeatBit is a free, open-source solution that simplifies feature flag management. It provides developers with a centralized platform for organizing and tracking feature flags across environments and projects. Key benefits of FeatBit include:
a. Centralized Management: FeatBit offers an organized approach to managing feature flags, reducing technical debt associated with their maintenance and updates.
b. Consistency: FeatBit encourages consistent naming conventions and organization for feature flags, promoting a clean and manageable codebase.
c. Auditing and Monitoring: Built-in features enable developers to track changes to feature flags and monitor usage, helping identify and remove unused or obsolete flags.
d. Integrations and Extensibility: FeatBit supports integration with popular development tools and platforms and allows for customization, ensuring seamless incorporation into your development workflow.
Conclusion
In summary, feature flags can play a significant role in addressing technical debt by providing a more controlled and flexible development environment. By promoting better development practices, incremental releases, and efficient code management, feature flags can contribute to a cleaner and more maintainable codebase. Using FeatBit as a streamlined, open-source solution for managing feature flags can further enhance this process, ensuring a more effective approach to reducing technical debt.